
There are many important factors that you should consider when choosing the top Georgia high schools. Some of these factors include CCRPI scores, membership in GHSA, number of students, and funding. These tips will help you choose the right school for your child. You can view the most recent reports from each school as well their CCRPI scores.
CCRPI scores
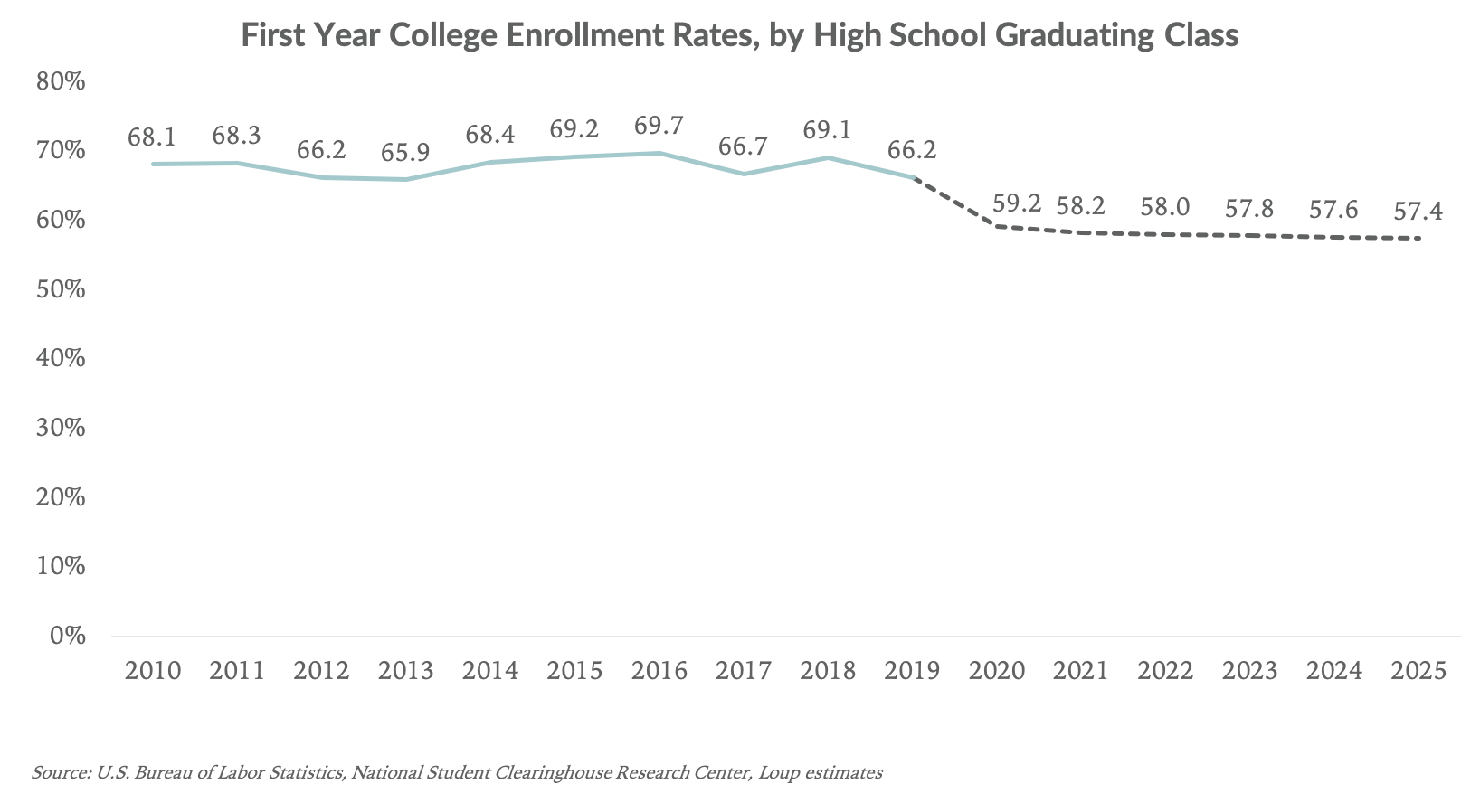
Georgia's state education department recently released its first CCRPI scores for high schools. The CCRPI, or College and Career Readiness Performance Index, measures student performance and college readiness. This measure replaces AYP, the federally mandated Adequate Yearly Progress. Georgia schools were granted a waiver by the No Child Left Behind Act. New system is designed to make these scores comparable.
The CCRPI reporting platform provides information on school, district and state performance. It was developed to assist educators, parents, community stakeholders, and others in understanding the performance of students. These reports are created using the results of annual standardized testing.
Membership in GHSA
The Georgia High Schools Association is a voluntary association of high schools in the state. Its members include 407 public and 56 private schools. Its main purpose is to promote education and sportsmanship as well as appreciation for the arts. To this end, it organizes championship events in 11 sports for boys, 15 sports for girls, and five coed sports.
The Association is managed by a Board. The Board of Directors includes the President-elect (or Vice-President), the Treasurer, and directors representing each of the five Districts. Each board has the power to make decisions and conduct business on all matters pertaining to the Association. The GSBA also employs an executive director.
Number of students attending each school
Georgia has over 521,000 high school students. There are 808 high schools, both public and private. Georgia has the sixth highest per-school graduation rate, at 79.4%. Georgians still have the lowest college graduation rates in the nation. Georgian students pay $28,653 per semester for tuition.
This has led many students to look into online high schools. It is now more important than ever to find an online high school that works. Many high school students are turning to online learning, as many public schools lack the necessary staffing and have insufficient teachers. Excel High School Online is a great place to begin, as it offers high school credit online.

Funding for each school
Georgia must modernize its school funding formula in order to ensure equity in education. It should prioritize students and teachers. A state Senate committee is currently studying the Quality Basic Education formula. It dates back to the 1980s. Funding for public education can be shared between the state and the local governments. The local part is based in property taxes. These vary depending upon the wealth of the community.
Georgia has nearly $9 billion in direct funding for schools districts. This includes $274 million for elementary and middle school students and $33 million for high school students.
FAQ
Do you need to go to college to become an early childhood educator?
Yes, but you may consider attending college to help prepare for a career.
It is essential to understand that becoming a teacher takes hard work. There are lots of applicants who aren't accepted into programs each year. Many people also leave college after only one semester.
A teacher must meet all requirements.
What's the difference between a university and a college?
A university provides higher education. It offers both undergraduate and graduate courses in many fields.
A college is typically smaller and less well-known than a university. It may offer fewer courses but often has its own specialist departments.
Is it difficult for a teacher to become?
Becoming a teacher requires a major commitment. Your studies will require a lot of your time.
You should expect to work around 40 hours per week while pursuing your degree.
You will also need to find a job that suits your schedule. Many students have difficulty finding part-time work that allows them to balance schoolwork and their personal lives.
You will likely teach classes once you have been hired as a full time teacher. You may also need to travel between schools each week.
What does it mean to be a teacher in early childhood education?
A teacher in early childhood education must have specific training. Most states require teachers to be certified by their state boards before they can work in public schools.
Some states require teachers to pass tests on subjects like math and reading.
Some states require teachers who teach early childhood education to have completed a certain amount of coursework.
Most states set minimum requirements for what a teacher should know. However, these requirements vary widely between states.
How much time should I devote to college preparation?
The time it takes to prepare to go to college will depend on how much time you are willing to dedicate to your studies. Start taking college preparation courses as soon as you finish high school if you want to be able to go straight to college. On the other hand, if you plan to take several years off before attending college, you probably don't need to begin planning until later.
It is important to discuss your plans and ideas with your parents, teachers, and other family members. You may be able to suggest courses of study. You should keep track of which courses you took and what grades you got. You'll be able to see exactly what you need next year.
Should I be a specialist or branch out in one area?
Many students prefer to focus on one subject, such as English, History, Math, rather than branching out into other subjects. It's not necessary to be a specialist. For example, if you're considering becoming a physician, you could choose to specialize in either internal medicine or surgery. You could also choose to specialize in family practice, pediatrics, gerontology or neurology. A business career could include sales, finance and marketing. The choice is yours.
Statistics
- Among STEM majors, that number is 83.5 percent. (bostonreview.net)
- Think of the rhetorical power of nineteenth-century abolitionist Harriet Beecher Stowe, Martin Luther King, Jr., or Occupy Wall Street activists with their rallying cry of “we are the 99 percent.” (bostonreview.net)
- Data from the Department of Education reveal that, among 2008 college graduates, 92.8 percent of humanities majors have voted at least once since finishing school. (bostonreview.net)
- In most developed countries, a high proportion of the population (up to 50%) now enters higher education at some time in their lives. (en.wikipedia.org)
- They are more likely to graduate high school (25%) and finish college (116%). (habitatbroward.org)
External Links
How To
What is vocational education?
Vocational Education prepares students for work by giving them skills that are required for a specific job, such as welding. It includes training on the job in apprenticeship programs. Vocational education differs from general education because it focuses on preparing individuals for specific careers rather than learning broad knowledge for future use. Vocational education does more than prepare for university. It helps people find jobs after graduation.
Vocational education can take place at all levels of schooling. This includes primary schools, secondary schools and colleges, universities as well as colleges, technical institutes, technical colleges, trade schools, community college, junior colleges, four-year colleges, and colleges. You can also find specialized schools such a culinary arts school, nursing school, law school, medical schools or dental schools. Many of these schools offer both academic instruction and practical experiences.
A number of countries have made significant investments in vocational education over recent decades; for example, Australia, Denmark, Finland, Germany, Ireland, Japan, Luxembourg, New Zealand, Norway, Poland, Sweden, Switzerland, the United Kingdom, and the United States. The effectiveness of vocational training is still a controversial topic. Some critics say it does not improve students' employability. Other argue that it prepares them well for life beyond school.
According to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics (47% of American adults are currently holding a postsecondary certificate/degree related to their current job), this figure is higher among those with more education. This number is higher for those with higher education. 71% of 25-29-year-olds have a bachelor's or higher degree and are employed in areas that require postsecondary credentials.
According to the BLS in 2012, almost half of Americans had at the least one type of postsecondary credential. About one-third of Americans held a two-year associate degree, while about 10 percent held a four-year bachelor's degree. One in five Americans holds a master’s degree or doctorate.
The median annual wage for individuals with a bachelor's in 2013 was $50,000. This was compared to $23,800 when they had no degree. The median wage for advanced degrees holders was $81,300.
The median wage for those who didn't complete high school was $15,200. The median annual income for those with less than a high-school diploma was $13,000